welding noun /ˈwel.dɪŋ/ n [U] the activity of joining metal parts together
(Definition of welding noun from the Cambridge Advanced Learner’s Dictionary)
Welding in industry has huge spectrum! it starts for arc welding, to fusion welding, to Laser and so on and so forth,
Generally, pressure vessel speaking, we use following three type of welding
– SMAW : Shielded Metal Arc Welding
– SAW : Submerged arc welding
– TIG : Tungsten Inert Gas welding
– GMAW : Gas Metal Arc Welding
Other types are
-Atomic Hydrogen Welding(AHW)
-Bare Metal ArcWelding(BMAW)
-Carbon ArcWelding(CAW)
-Electro Gas Welding(EGW)
-Electro Slag Welding(ESW)
-Plasma Arc Welding(PAW)
-Stud Arc Welding(SW)
Lets discuss Generall Welding Process in Brief
SMAW :
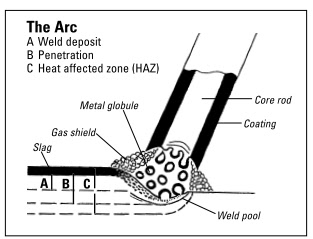
As you can see in picture, the arc is created between Parent material and electrode. The oxidation is avoided by the flux coated on electrode. Due to arc the weld metal start melting, and due to high temperature, the flux also get melted, due to density difference, the flux floats over weld pool, and thus by function makes a barrier between atmosphere & weld to avoid any oxidation.
The temperature found in arc is as high as 7000ºC, at which the gas/air get ionized, providing good electrical conductivity in the arc.
The actual transfer of metal from the electrode to the workpiece is in the form of molten globules of different sizes depending on the type of electrode used. Some electrodes produce globules that are so large that they actually shortcircuit the arc for a moment.
Electrodes for manual arc welding (sometimes referred to as stick welding) consist of a rod and a coating material. As a rule, the alloy in the rod will be similar to the material to be welded.
The most common types of electrodes are:
1. The Organic type (electrodes contain large quantities of organic substances such as cellulose)
2. The Rutile type (electrodes contain large quantities of the mineral rutile)
3. The Acid type (electrodes produce an Iron Oxide / Manganese Oxide / Silica type of slag, the metallurgical character which is an acid.)
4. The Basic type (Low Hydrogen)
5. LMA (Low moisture absorption electrode)
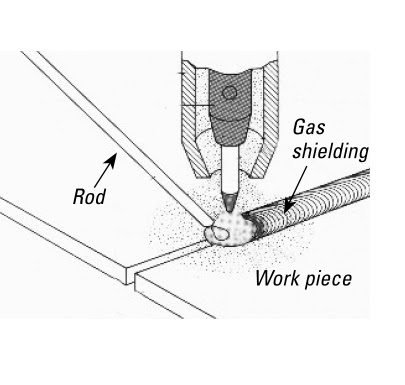
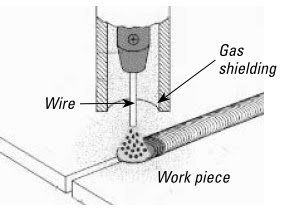
TIG Welding:

SEO